Expert Treatment for Thyroid Swelling (Goiter) in Chennai
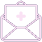
Thyroid swelling, commonly known as a goiter, refers to the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. This condition can arise from a variety of thyroid disorders, and it may present itself as a minor, harmless lump or develop into a significantly enlarged gland that causes discomfort, swallowing difficulties, or breathing issues.
Dr. Thalavai Sundarram, a highly experienced endocrinologist in Chennai, offers expert treatment for thyroid swelling. He specialises in both medical and surgical management of thyroid diseases, ensuring patients receive comprehensive and personalised care for goiter and related thyroid conditions.
Causes of Thyroid Swelling
Iodine Deficiency
Insufficient iodine in the diet can lead to enlargement of the thyroid gland.Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Excess hormone production can result in gland enlargement.Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
The gland may swell as a compensatory response to low hormone levels.Thyroid Nodules
Lumps or growths in the thyroid can lead to localised swelling.Thyroiditis
Inflammation caused by infection or autoimmune disorders can contribute to swelling.Graves' Disease
This autoimmune condition stimulates overactivity in the thyroid, leading to swelling.
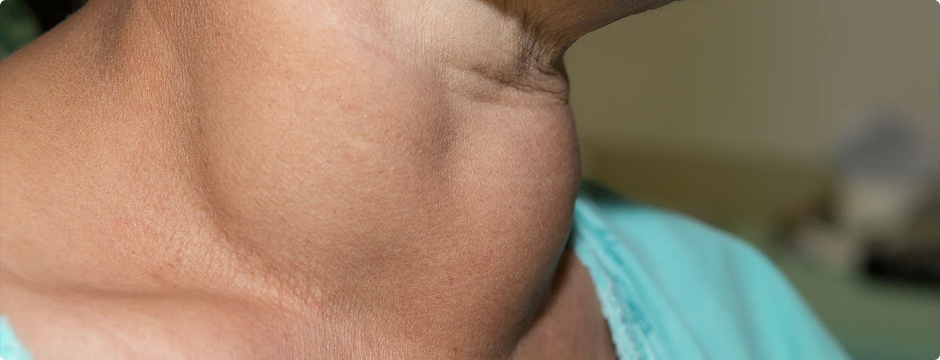
Recognising the Symptoms of Thyroid Swelling
Visible Neck Swelling

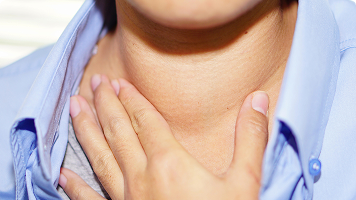
Difficulty Swallowing

Breathing Difficulties

Voice Changes
Throat Tightness
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
Hypothyroidism Symptoms
Diagnosis of Thyroid Swelling
- Physical Examination – Assessing the size, texture, and tenderness of the thyroid.
- Thyroid Function Tests – Measuring levels of TSH, T3, and T4 hormones.
- Ultrasound – Evaluating the gland's size, shape, and presence of nodules.
- Radioactive Iodine Scan – Identifying areas of overactivity or underactivity in the thyroid.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy – Testing nodules for cancerous or abnormal cells.
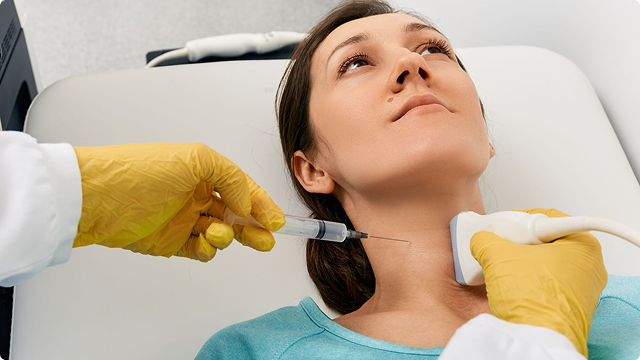
Top Treatments for Thyroid Swelling
Iodine Supplementation
Effective when swelling is caused by iodine deficiency, helping to restore proper thyroid function.
Medications
Anti-thyroid drugs manage hyperthyroidism, while hormone replacement therapy treats hypothyroidism to regulate hormone levels.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Used to shrink an overactive thyroid, reducing swelling and restoring normal function.
Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
In cases of large or cancerous swellings, partial or total removal of the thyroid gland may be necessary.
Monitoring
Small, non-disruptive goiters may only require regular observation to ensure no complications arise.
Outcomes of Thyroid Swelling Treatment
- Reduces swelling and alleviates pressure on the throat
- Restores proper thyroid function and hormonal balance
- Prevents complications related to thyroid dysfunction
- Requires consistent follow-ups to ensure effective long-term management
Complications of Untreated Thyroid Swelling
Neglecting persistent thyroid swelling can lead to several severe complications. An enlarged thyroid can compress the windpipe or esophagus, resulting in difficulties with breathing and swallowing. Moreover, untreated hormonal imbalances, such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, can worsen over time, significantly impacting overall health. Certain thyroid swellings may also indicate the presence of thyroid cancer, highlighting the importance of timely evaluation. Additionally, the swelling itself, known as a goiter, can continue to grow, leading to increased discomfort and further complications.
Managing Thyroid Swelling for Long-Term Health
Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for effective management of thyroid swelling. Regular monitoring, targeted medical intervention, and a balanced diet can help prevent complications and support thyroid health.
If you notice persistent neck swelling or discomfort, consulting a healthcare professional for a thorough thyroid evaluation can ensure you receive the timely care you need.

Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Thalavai Sundarram
Endocrinologist
M.S., M.Ch (Endocrine Surgery) FARIS
BOOK APPOINTMENT