Comprehensive Care for Hyperthyroidism in Chennai
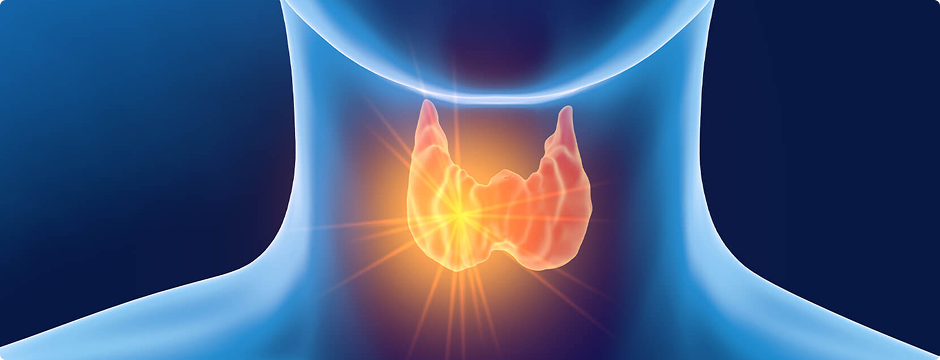
Hyperthyroidism is a serious condition characterised by excessive production of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland, resulting in an overactive metabolism. This can lead to significant weight loss, heightened heart rate, and heightened anxiety. Without proper treatment, hyperthyroidism poses severe risks that can affect the heart, bones, and overall well-being.Dr. Thalavai Sundarram provides expert hyperthyroidism treatment in Chennai, ensuring safe and effective management of this condition.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Graves’ Disease
An autoimmune disorder that leads to the body producing too much thyroid hormone.Thyroid Nodules
These are lumps that can grow in the thyroid gland and produce hormones independently.Excess Iodine Intake
Consuming too much iodine through diet or medications can cause the thyroid to become overly active.Thyroiditis
Inflammation of the thyroid can lead to temporary spikes in hormone levels.
Recognising the Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism

Unintended Weight Loss

Rapid Heartbeat (Tachycardia)

Anxiety & Irritability

Excessive Sweating & Heat Intolerance
Tremors

Frequent Bowel Movements

Sleep Disturbances
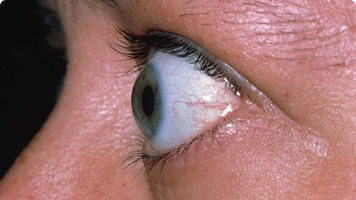
Bulging Eyes (Exophthalmos)
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
- TSH Test (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) – Low levels of TSH suggest an overactive thyroid.
- T3 and T4 Tests – Elevated hormone levels confirm hyperthyroidism.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test – This assesses thyroid activity and can identify Graves’ disease.
- Thyroid Ultrasound – Used to detect nodules or inflammation within the thyroid.
Top Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
Anti-Thyroid Medications
Medications like Methimazole and Propylthiouracil (PTU) work by reducing excessive thyroid hormone production, helping to restore hormonal balance.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
A highly effective treatment that selectively destroys overactive thyroid cells, leading to long-term regulation of hormone levels.
Beta-Blockers
While not addressing the underlying condition, these medications help control symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, and anxiety, improving overall comfort.
Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
In severe or treatment-resistant cases, partial or total removal of the thyroid gland may be necessary to eliminate excessive hormone production.
Outcomes of Hyperthyroidism Treatment
- Restores normal hormone levels and stabilizes metabolism
- Reduces symptoms like rapid heartbeat, tremors, and anxiety
- Prevents severe complications such as heart disease and osteoporosis
- Requires careful monitoring to ensure long-term effectiveness and well-being
Complications of Untreated Hyperthyroidism
If left unaddressed, hyperthyroidism can lead to life-threatening complications affecting multiple organ systems. One of the most severe risks is a thyroid storm, a sudden and extreme surge in thyroid hormones that can cause fever, confusion, and heart failure, requiring immediate medical attention. The condition also significantly increases the risk of heart problems, including atrial fibrillation, high blood pressure, and potential heart failure.
Additionally, prolonged hormone excess can weaken bones, leading to osteoporosis and a higher likelihood of fractures. In cases of Graves’ disease, hyperthyroidism can cause eye-related complications such as double vision, light sensitivity, and bulging eyes, impacting both vision and overall quality of life.
Managing Hyperthyroidism for Optimal Health
Timely diagnosis and effective treatment enable individuals with hyperthyroidism to enjoy a fulfilling life. Consistent monitoring, adherence to prescribed therapies, and lifestyle changes are vital for stabilising hormone levels and preventing complications.
If you notice any symptoms related to thyroid dysfunction, seeking a professional evaluation can facilitate early detection and successful management of hyperthyroidism. Your health is worth it!

Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Thalavai Sundarram
Endocrinologist
M.S., M.Ch (Endocrine Surgery) FARIS
BOOK APPOINTMENT