Hormonal Imbalance & Pituitary Disorder Care in Chennai
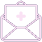
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the "master gland," plays a crucial role in regulating vital hormones that influence growth, metabolism, stress responses, and reproductive functions. When this gland produces too much or too little of certain hormones, it can lead to various health challenges known as pituitary hormone disorders. Dr. Thalavai Sundarram offers expert treatment for pituitary hormone disorders in Chennai, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective hormonal management.
Causes of Pituitary Hormone Disorders
Pituitary Tumors
Both benign and malignant growths can significantly affect hormone production.Genetic Mutations
Inherited disorders that impair gland function.Head Injury
Trauma that can severely damage hormone regulation.Autoimmune Diseases
Conditions where the body’s immune system targets the pituitary gland.Infections or Inflammation
Conditions like meningitis, tuberculosis, or sarcoidosis that impact gland health.Radiation Therapy
Treatments for brain tumors that can disrupt hormone secretion.
Common Pituitary Hormone Disorders
Acromegaly
Resulting from excessive growth hormone, leading to enlarged extremities.Cushing’s Disease
Caused by overproduction of cortisol due to excessive ACTH.Prolactinoma
A benign tumor that causes increased prolactin levels, affecting fertility.Diabetes Insipidus
Characterised by a shortage of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), resulting in excessive thirst and urination.Hypopituitarism
Characterised by insufficient hormone production, leading to multiple hormone deficiencies.Growth Hormone Deficiency
Results in stunted growth in children and fatigue or muscle loss in adults.
Symptoms of Pituitary Hormone Disorders

Weight fluctuations

Persistent fatigue
Irregular menstrual cycles

Excessive thirst

Vision changes
Diagnosis of Pituitary Hormone Disorders
- Blood Tests – To evaluate hormone levels like cortisol and growth hormone.
- MRI or CT Scan – Imaging techniques used to identify tumors or anatomical issues.
- Stimulation or Suppression Tests – To analyse the pituitary gland’s hormone response.
- Vision Tests – To check for optic nerve pressure due to tumors.
Top Treatments for Pituitary Hormone Disorders
Medications
Depending on the condition, hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed to restore deficient hormones, while medications like dopamine agonists or somatostatin analogs help suppress excess hormone production.
Surgery (Transsphenoidal Surgery)
The preferred approach for removing pituitary tumors, particularly when they threaten vision or cause severe hormonal imbalances. Advanced microsurgical and endoscopic techniques ensure precision and faster recovery.
Radiation Therapy
Recommended when surgery isn't feasible or if tumors recur. Targeted radiation techniques, such as stereotactic radiosurgery (Gamma Knife), minimise damage to surrounding brain structures.
Outcomes of Specialised Pituitary Disorder Treatment
- Restored Hormonal Balance – Proper management helps regulate essential bodily functions.
- Vision Preservation – Early intervention prevents optic nerve compression and vision loss.
- Reduced Tumor Recurrence – Advanced treatments ensure long-term control and improved quality of life.
Managing Pituitary Hormone Disorders for Better Health
Proactive diagnosis and strategic treatment can effectively alleviate symptoms and enhance quality of life. Regular monitoring and check-ups are crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and preventing potential complications. Taking charge of your health can lead to profound improvements in your well-being.

Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Thalavai Sundarram
Endocrinologist
M.S., M.Ch (Endocrine Surgery) FARIS
BOOK APPOINTMENT