Advanced Thyroid Cancer Treatment in Chennai
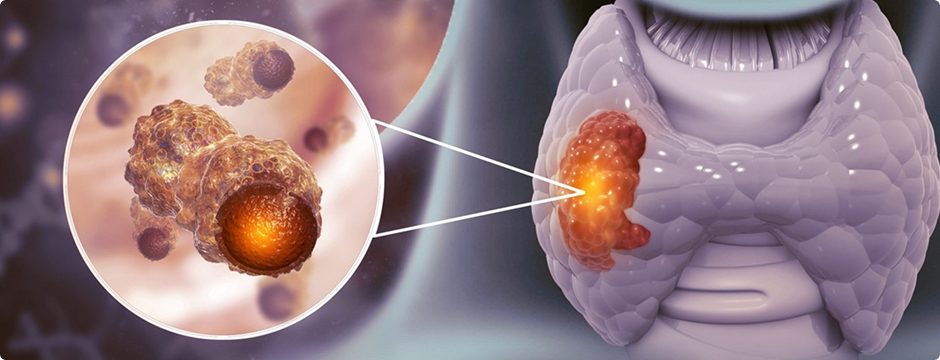
Thyroid cancer arises when abnormal cells proliferate uncontrollably in the thyroid gland, resulting in a tumor. Though many forms of thyroid cancer grow slowly and are manageable, early detection is vital for achieving optimal outcomes. Understanding the different types of thyroid cancer, along with their severity and progression, can empower individuals to seek timely medical attention. Dr. Thalavai Sundarram offers expert thyroid cancer treatment in Chennai, providing advanced care tailored to each patient’s condition.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is categorised into various types based on its aggressiveness
Papillary Thyroid Cancer
The most prevalent type, known for its slow growth and high treatability.Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Slightly more aggressive than papillary, yet still highly treatable.Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC)
A rare variant often associated with genetic predispositions.Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
A rare and very aggressive form that can spread rapidly.
Common Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Swelling in the neck

Difficulty swallowing
Persistent hoarseness
Neck pain
Swollen lymph nodes

Breathing difficulties
Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer
- Physical Examination – Assessing for lumps or swelling in the neck.
- Thyroid Function Tests – Evaluating hormone levels to gauge thyroid function.
- Ultrasound – Distinguishing between solid and fluid-filled lumps.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy – Obtaining tissue samples for detailed analysis.
- Molecular Testing – Identifying genetic mutations that could indicate aggressive thyroid cancers.
- CT, MRI, or PET Scans – Determining if the cancer has metastasised beyond the thyroid.

Top Treatments for Thyroid Cancer
Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
Involves partial or total removal of the thyroid gland to eliminate cancerous tissue.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy (RAI)
Effectively destroys any remaining cancerous thyroid cells after surgery.
Hormone Therapy
Replaces thyroid hormones and helps prevent cancer recurrence by suppressing TSH levels.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Used in advanced cases to block the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy
Recommended when surgery isn’t an option or for treating high-risk cancers.
Chemotherapy
Rarely used, except in aggressive cases like anaplastic carcinoma.
Outcomes of Thyroid Cancer Treatment
- Eliminates cancerous cells and reduces the risk of recurrence
- Restores hormonal balance through thyroid hormone replacement therapy
- Improves survival rates, especially with early detection and treatment
- Requires ongoing monitoring to ensure long-term effectiveness
Complications of Untreated Thyroid Cancer
Untreated thyroid cancer can result in serious complications. The cancer may spread to nearby tissues, invading lymph nodes, the trachea, or the esophagus. In advanced stages, metastasis can occur, leading to the spread of cancer to distant organs such as the lungs and bones.
Furthermore, the progression of the tumor can obstruct airways and the digestive system, causing significant breathing and swallowing difficulties. If the thyroid is completely removed during treatment, lifelong hormone replacement therapy becomes necessary to manage the resulting hormonal imbalance.
Early Detection and Long-Term Management
The prognosis for thyroid cancer is notably positive, especially with early intervention. Routine check-ups, imaging tests, and hormone monitoring are critical in managing the disease effectively.
If you notice persistent neck swelling, changes in your voice, or trouble swallowing, seeking prompt medical care is essential. Early detection can lead to effective treatment and a positive outcome. Don’t hesitate—take control of your health today!

Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Thalavai Sundarram
Endocrinologist
M.S., M.Ch (Endocrine Surgery) FARIS
BOOK APPOINTMENT